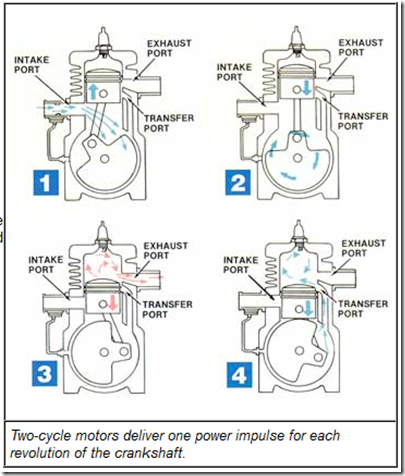
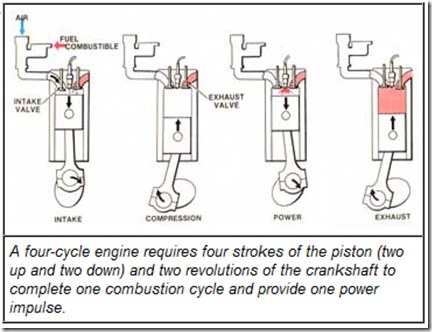
Amsoil Snowmobile Oil
Buy online, or get a FREE Amsoil Catalog
See all Amsoil snowmobile oil products here.
INTERCEPTOR™ High Performance Synthetic 2-Cycle Oil (AIT)
A high-performance two-cycle oil with a performance emphasis on exhaust power valves. Excellent for all types of snowmobiles, motorcycles, personal watercraft, ATVs and jet boats. Contains high levels of detergent additives to prevent valve sticking. High quality replacement for manufacturer branded oils. Injector use or 50:1 premix. JASO FC, API TC
Amsoil Snowmobile Oil
Amsoil Snowmobile Oil AMSOIL INTERCEPTOR™ Synthetic 2-Cycle Oil is formulated with a proprietary blend of the finest synthetic base oils and additives available today. This unique AMSOIL Chemistry represents a breakthrough development in the field of two-cycle engine lubrication. The backbone of AMSOIL INTERCEPTOR 2-Cycle Oil is a specially developed molecularly saturated synthetic base oil. This, combined with a robust additive package, ensures exceptional lubricity, cleanliness and optimum clean-burning characteristics. Extensive research and testing, including a full snowmobiling season in severe Rocky Mountain applications, has proven that wear on cylinders, pistons and bearings is significantly reduced. And with up to 30 percent more detergency and dispersancy additives than typical two-cycle oils, Amsoil Snowmobile Oil AMSOIL INTERCEPTOR virtually eliminates hard carbon deposits that cause exhaust power valve sticking, ring sticking and preignition-promoting “hot spots” in the combustion chamber.
- Helps prevents hard carbon deposits that cause exhaust power valve sticking and ring sticking.
- Superior lubricity controls cylinder, piston and bearing wear.
- Reduces smoke and odor associated with two-cycle engines.
- Helps prevent plug fouling.
- Provides exceptional SAE #4 cold temperature fluidity (-58°F pour point).
- Versatile and excellent for all types of recreational equipment.
- Protects against rust.
- Helps prevent pre-detonation from combustion chamber “hot spots.”
Amsoil Snowmobile Oil
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
AMSOIL INTERCEPTOR Synthetic 2-Cycle Oil is formulated with a proprietary blend of the finest synthetic base oils and additives available today. This unique AMSOIL chemistry represents a breakthrough development in the field of two-cycle engine lubrication.
The backbone of AMSOIL INTERCEPTOR 2-Cycle Oil is a specially developed molecularly saturated synthetic base oil. This, combined with a potent additive package, ensures exceptional lubricity, cleanliness and optimum clean-burning characteristics. Extensive research and testing, including a full snowmobiling season in severe Rocky Mountain applications, has proven that wear on cylinders, pistons and bearings is dramatically reduced. And with up to 30 percent more detergency and dispersancy than typical two-cycle oils, AMSOIL INTERCEPTOR virtually eliminates damaging deposits on piston skirts, ring grooves and exhaust power valves.
APPLICATIONS
AMSOIL INTERCEPTOR Synthetic 2-Cycle Oil is recommended as an injector oil or at a 50:1 mix ratio in carbureted, electronic fuel Injected (EFI) and direct fuel injected (DFI) snowmobiles, personal watercraft, motorcycles, ATVs and jet boats, including, but not limited to, those manufactured by Bombardier®, Yamaha®, Arctic Cat®, Polaris®, Kawasaki®, Suzuki® and Honda®.
It is recommended wherever JASO FC or API TC two-cycle oils are specified. INTERCEPTOR is a premium quality replacement for recreational equipment manufacturers’ branded two-cycle oils. It is compatible with most mineral and synthetic two-cycle oils, however, for best performance, mixing oils should be minimized.
400,000 Miles of Severe Snowmobile Field testing With No Deposit Buildup, Power Valve Sticking, Ring Sticking or Engine Failures.
Subjected to adverse field testing conditions in the Rocky Mountains, including long trail rides, high RPM powder riding and steep hill climbs, AMSOIL INTERCEPTOR demonstrated superior wear protection and outstanding deposit control.
.
No carbon deposits are detectable in the functioning region of the exhaust power valves, resulting in “no stick” performance, continuous valve operation and reduced maintenance.

Pistons show no scoring, little or no wear and no heavy deposits, and wrist pins show no discoloration from heat. In fact, the original machine markings on the pistons are still visible.
Cylinder head is clean with no deposits, preventing pre-ignition problems.
http://www.syntheticoilhq.com/blog
WordPress Tags: AMSOIL,INTERCEPTOR,Snowmobile,FREE,Catalog,products,High,Performance,Synthetic,Cycle,emphasis,Excellent,ATVs,valve,replacement,manufacturer,Injector,JASO,Chemistry,development,engine,characteristics,Extensive,Rocky,Mountain,combustion,chamber,Superior,cylinder,odor,temperature,Versatile,equipment,detonation,PRODUCT,DESCRIPTION,ratio,Bombardier,Yamaha,Arctic,Polaris,Kawasaki,Suzuki,Honda,mineral,Miles,Severe,Field,Deposit,Buildup,Power,hill,protection,boats,cylinders,manufacturers,Failures,Mountains,snowmobiles,motorcycles,watercraft,proprietary,lubrication,pistons,detergency,dispersancy,carbon,piston